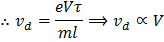A potential difference is applied across the ends of a metallic wire. If the potential difference is doubled, the drift velocity will
a)
Be doubled
b)
Be halved
c)
Be quadrupled
d)
Remain unchanged
A potential difference is applied across the ends of a metallic wire. If the potential difference is doubled, the drift velocity will
a)
Be doubled
b)
Be halved
c)
Be quadrupled
d)
Remain unchanged
Question ID - 150308 | SaraNextGen Answer
A potential difference is applied across the ends of a metallic wire. If the potential difference is doubled, the drift velocity will
a)
Be doubled
b)
Be halved
c)
Be quadrupled
d)
Remain unchanged
|
A potential difference is applied across the ends of a metallic wire. If the potential difference is doubled, the drift velocity will |
|||||||
|
a) |
Be doubled |
b) |
Be halved |
c) |
Be quadrupled |
d) |
Remain unchanged |
|
(a) Drift velocity is defined as the average velocity with which free electrons get defined towards the positive end of the conductor under the influence of an external electric field. Drift velocity is given by
(if
So, when the potential difference is doubled the drift velocity will be doubled. |

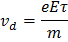
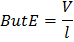
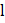 is length of the conductor and V is constant potential difference applied across the ends of the conductor)
is length of the conductor and V is constant potential difference applied across the ends of the conductor)