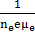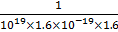Mobility of electrons in a semiconductor in defined as the ratio of their drift velocity of the applied electric field. If, for an n-type semiconductor, the density of electrons is 1019m−3 and their mobility is 1.6m2(v.s) then the resistivity of the semiconductor(since it is an n-type semiconductor contribution of holes is ignored) is close to:
|
a. |
2 Ωm |
b. |
0.4 Ωm |
|
c. |
4 Ωm |
d. |
0.2 Ωm |
Question ID - 50050 | SaraNextGen Answer Mobility of electrons in a semiconductor in defined as the ratio of their drift velocity of the applied electric field. If, for an n-type semiconductor, the density of electrons is 1019m−3 and their mobility is 1.6m2(v.s) then the resistivity of the semiconductor(since it is an n-type semiconductor contribution of holes is ignored) is close to:
a.
2 Ωm
b.
0.4 Ωm
c.
4 Ωm
d.
0.2 Ωm
Mobility of electrons in a semiconductor in defined as the ratio of their drift velocity of the applied electric field. If, for an n-type semiconductor, the density of electrons is 1019m−3 and their mobility is 1.6m2(v.s) then the resistivity of the semiconductor(since it is an n-type semiconductor contribution of holes is ignored) is close to:
|
a. |
2 Ωm |
b. |
0.4 Ωm |
|
c. |
4 Ωm |
d. |
0.2 Ωm |

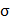 E=nevd
E=nevd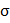 =ne
=ne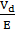
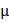
 =p =
=p =